I got a new Alecto DKW-2012 weather station as a birthday present and all was well again (at least for a while...)
One feature both weather stations lacked is logging of data over longer periods. And so a new project was born, using a Raspberry Pi to gather weather related sensor data and store it in a database on my home server. The broken weather station was hacked in all possible ways (new pressure, humidity and temperature sensor) and was mounted next to my other station.
 |
| Left: the hacked weather station Right: Alecto DKW-2012 |
Apart from looking a bit silly having two weather stations mounted next to eachother, the indoor unit also suffers from reception problems every now and then.
Wouldn't it be nice to have a single weather station that logs all of its data and at the same time display this data on the wireless indoor display?
I searched the net for any info on the Alecto DKW-2012. The line of Alecto weather stations is very similar (or identical) to units produced by Fine Offset Electronics. They operate at 868.3MHz and are reported to use either FSK or OOK modulation.
Using a DVB-T USB stick I was able to capture the data sent by the base station.
| Complete weather data message |
| Start of message |
- All data is sent using OOK modulation
- Bitrate is 2kbit/s (the short yellow stripes show the bit time of 500us)
- On air, a binary '1' is encoded as 100 and a binary '0' as 11100
- The preamble is 0xFF
- A complete message consists of 11 bytes (including preamble)
- Messages duration varies, depending on its content, roughly between 130 and 220 ms.
Some code found on the web details the protocol (e.g. nodo) but I couldn't find any project that transmits weather data. I did however find some code by SevenWatt that uses an Arduino and RFM69W to transmit OOK modulated signals.
Using this code as a base, a Moteino with RFM69W and the DVB-T USB stick to analyze the actual on-air data I was able to take control of my wireless indoor display!
 |
| 'Possessed' DKW-2012 weather display |
Next step was to actually get some real values from my hacked weather station on the display. My home server, which stores the weather data in a database, also publishes this data to an MQTT broker. A Node-RED installation subscribes to this data and re-publishes each value to topics recognized by an MQTT MySensors Gateway which I wrote some time ago. The gateway distributes these values to wireless sensor nodes in a MySensors network.
I hooked up an nRF24L01+ to the Moteino to be able to communicate with the MySensors network, using the following connections:
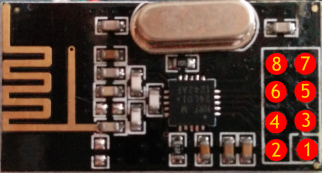 |
| nRF24L01+ module pinout |
| Function | Moteino pin | nRF24L01+ pin | |
|---|---|---|---|
GND
|
GND
|
-
|
1
|
3.3V
|
3.3V
|
-
|
2
|
CE
|
7
|
-
|
3
|
CSN/CS
|
8
|
-
|
4
|
SCK
|
13
|
-
|
5
|
MOSI
|
11
|
-
|
6
|
MISO
|
12
|
-
|
7
|
IRQ
|
--
|
-
|
--
|
This Arduino sketch has the MySensors stack integrated and executes the following tasks:
- Configure both the RFM69W and the MySensors library
- Run 3 simultaneous statemachines:
- Request wallclock time from the MySensors Gateway and send this data as a DCF77 encoded message to the wireless display. This process repeats every hour.
- Request the weather data we're interested in (temperature, humidity, windspeed, gust, rain) from the Gateway. This triggers automatic subscription to the corresponding MQTT topics. Once the statemachine has received a value for each topic (and thus subscription to all topics has succeeded) it becomes dormant, waiting for new values to be published by the Gateway. When one or more values come in, it triggers the next statemachine:
- Send sensor data to the wireless display. If no new sensor data comes in for 1 minute, old data is repeated (to prevent the display from blanking after 6.5min without receiving new data)
 |
| The same hack also works for an Alecto WS-2900 display! |